Product
COB LED module
[Technical field]
The utility model relates to an LED module, and more specifically, to a COB (Chip on Board) LED module.
[Background technology]
LED, as a light source, has been increasingly widely used due to its own advantages. Among them, COB (Chip on Board) LED is the product of its continuous technological progress. COB LED is a chip on board package, which is one of the bare chip mounting technologies. The semiconductor chip is mounted on the printed circuit board, and the electrical connection between the chip and the substrate is achieved by the lead stitching method, and is covered with resin to ensure reliability. COB LED is also called COB LED source or COB LED module. This new type of COB LED has an increasingly wide range of applications due to its safety, reliability, high efficiency, energy saving, and environmental protection. As shown in Figure 1, the COB LED module commonly used in the industry at present has a structure in which a printed circuit board 2' is arranged on the surface of a substrate 1', an insulating layer 3' is arranged on the bottom surface of the circuit board, and an ink 4' is arranged on the top surface of the circuit board. The circuit layer 5' is arranged in the circuit board, and the side of the LED chip 6' with the pins is pasted on the top surface of the circuit board for electrical connection. Since there is an insulating layer between the circuit layer and the substrate for insulation, the heat of the LED chip cannot be directly transferred to the substrate, so the heat dissipation efficiency is low, resulting in a shorter service life of the entire LED module.
[Content of the utility model]
The technical problem to be solved by the utility model is to provide a COB LED module with higher heat dissipation efficiency in view of the problem of low heat dissipation efficiency of the COB LED module in the prior art.
The technical solution adopted by the utility model to solve its technical problem is: construct a COB LED module, including a substrate, a circuit board arranged on the substrate, and an LED chip electrically connected to the circuit board, the circuit board is provided with a mounting hole matching the LED chip, and the back side of the LED chip without pins is fixed to the substrate through the mounting hole. In the COB LED module of the utility model, the circuit board includes a printed board, a circuit layer arranged in the printed board, an insulating layer coated on the bottom of the printed board, and an ink layer coated on the top of the printed board, and the LED chip is electrically connected to the circuit layer of the circuit board. In the COB LED module of the utility model, an adhesive is also provided between the back side of the LED chip and the substrate. In the COB LED module of the utility model, the adhesive is an adhesive made of silver paste. In the COB LED module of the utility model, a mounting hole corresponding to the mounting hole position is provided on the substrate, and the LED chip is fixed in the mounting hole. In the COB LED module of the utility model, the substrate is an aluminum substrate. In the COB LED module of the utility model, a mounting groove matching the LED chip is provided on the substrate, and the LED chip is fixed in the mounting groove through the mounting hole of the circuit board.
The implementation of the COB LED module described in the utility model has the following beneficial effects: by opening a mounting hole on the circuit board, the LED chip is directly mounted on the substrate through the mounting hole, so that there is no insulation layer between the LED chip and the substrate, and the heat of the LED chip can be directly conducted to the substrate.
The utility model will be further described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[Drawings]
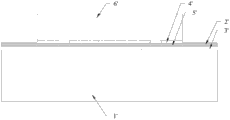
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the mounting structure of the COB LED module in the prior art;

Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the preferred embodiment of the COB LED module described in the utility model.
[Specific implementation]
As shown in Figure 2, in the preferred embodiment of the COB LED module described in the utility model, it includes a substrate 1, a circuit board 2 arranged on the substrate, and an LED chip 3 electrically connected to the circuit board. Among them, a mounting hole 21 is opened on the circuit board, and the shape and size of the mounting hole match the outer contour of the LED chip so that the LED chip can pass through the mounting hole during assembly. The LED chip is usually provided with a pin 31 for electrical connection on the bottom side, and the back side is wrapped with an insulating material to protect and insulate the chip. The back side of the LED chip without a pin is fixed to the substrate through the mounting hole. In this way, the heat generated by the LED chip can be directly transferred to the substrate, so that the heat dissipation efficiency of the entire module is high. In this preferred embodiment, the circuit board includes a printed board 22, a circuit layer 23 arranged on the printed board, an insulating layer 24 coated on the bottom of the printed board, and an ink layer 25 coated on the top surface of the printed board, wherein the LED chip is electrically connected to the circuit layer of the circuit board. In this preferred embodiment, the substrate is preferably set to an aluminum substrate 1a, because the aluminum substrate has good thermal conductivity and low cost. Preferably, a mounting groove 12 is set on the aluminum substrate, and the size and contour of the mounting groove match the LED chip so that the LED chip can be placed in the mounting groove and fixed. The LED chip can be fixed in the mounting groove by welding, and preferably an adhesive 32 is set between the back side of the LED chip and the substrate, and the back side of the LED chip is fixed to the substrate by the adhesive; wherein the adhesive is preferably made of silver paste with high thermal conductivity and insulation. The above-mentioned embodiments only express several implementation methods of the utility model, and the description is relatively specific and detailed, but it cannot be understood as a limitation on the patent scope of the utility model. It should be pointed out that, for those skilled in the art, several modifications and improvements can be made without departing from the concept of the utility model, and these are all within the scope of protection of the utility model. Therefore, the scope of protection of the utility model patent shall be based on the attached claims.